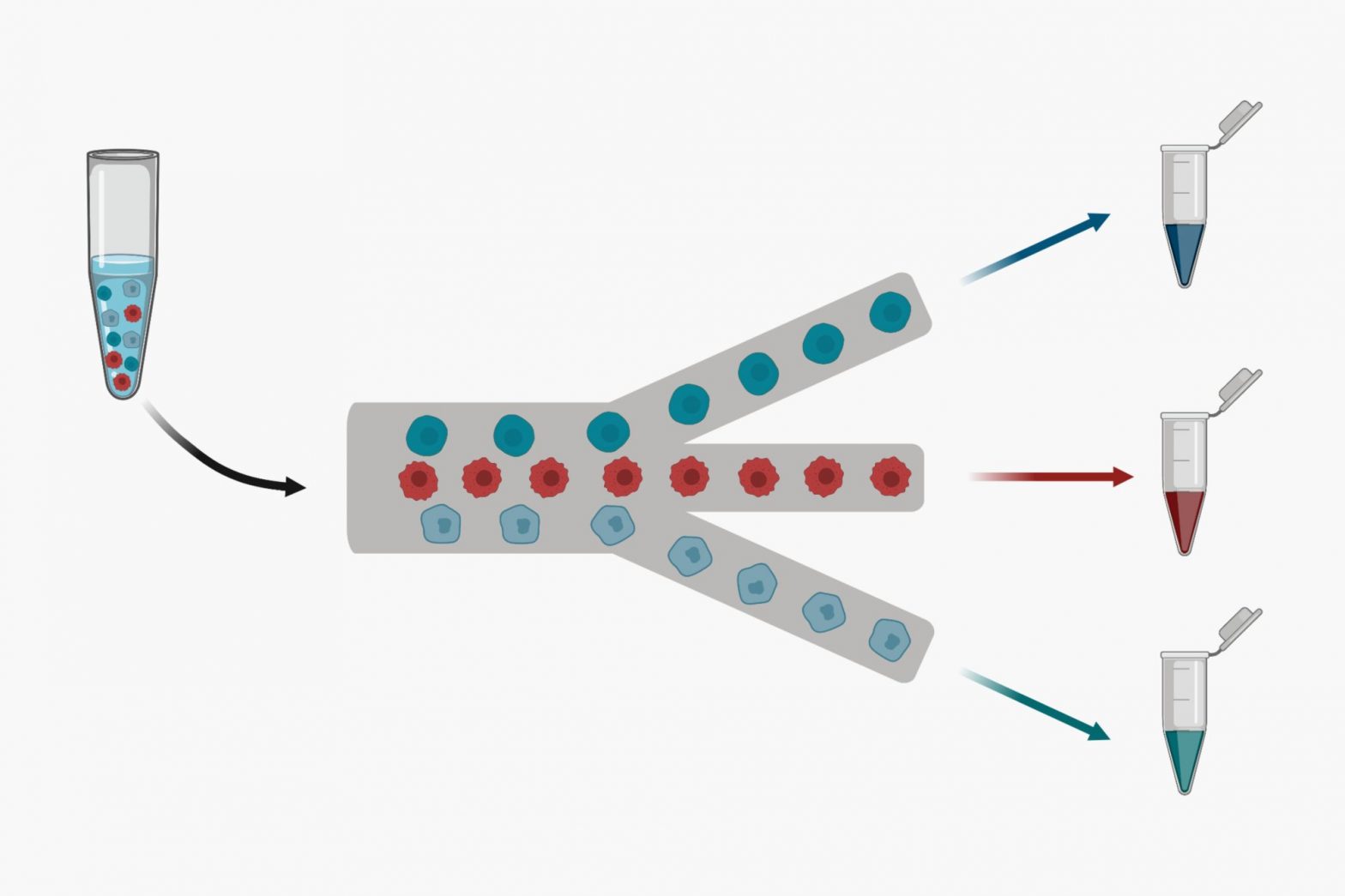
Cell separation refers to the process of isolating and separating specific types of cells from a mixture of cells. This can be done for various purposes, such as studying the function of individual cell types, producing pure cell populations for medical applications, or identifying specific cells for diagnostic purposes.
Cell separation plays an important role in various applications, including biologics designing & development, therapeutic protein production, in-vitro diagnostics, and other research applications such as capture circulating tumor cells in the blood, conduct molecular analysis of specific cell populations, isolate immune cells from peripheral blood, preparing a sample of blood separated from plasma, separate bacteria from food, study the effects of drug candidates on cell types, isolate white blood cells from tissue, recover mononucleated cells from the blood.
𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐚𝐭: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-toc-and-sample/14228
There are several methods used for cell separation, including physical, chemical, and biological methods. Physical methods rely on the physical properties of cells, such as size, density, and shape, to separate them. Examples of physical methods include centrifugation, filtration, and sedimentation.
Chemical methods use chemical properties, such as surface charge, to selectively bind and isolate cells. One example of a chemical method is immunomagnetic cell separation, which uses magnetic beads coated with antibodies to selectively bind to and isolate specific cell types.
Biological methods take advantage of the natural properties of cells, such as their ability to adhere to certain surfaces or their sensitivity to certain stimuli. One example of a biological method is fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), which uses fluorescent markers to label specific cells and a machine to sort them based on their fluorescence signal.
Overall, cell separation is an important technique used in many areas of biology and medicine to study and manipulate individual cell types.
𝐂𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐝-𝟏𝟗 𝐒𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐨:
- The COVID-19 pandemic disturbed the entire supply chain in the majority of industries worldwide. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has created a lucrative opportunity for researchers to study and understand this new infectious virus to develop treatments and diagnostic tools for it. Several pharmaceutical and biotech giants have been conducting rapid and extensive R&D activities to develop novel vaccines, therapies, and testing kits by using stem cells or regenerative medicine. This has significantly boosted the demand for cell separation tools in research applications.
- The governing board of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) approved USD 5 million in funding for peer-reviewed regenerative medicine and stem cell research that could quickly develop treatments for COVID-19. Stem Cell Network (SCN) is providing up to USD 500,000 in funding to support rapid response research that uses a stem cell or regenerative medicine approach for addressing COVID-19.
𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐬𝐞 𝐈𝐧𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐫𝐲: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/purchase-enquiry/14228
There are various segments used in cell separation, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some of the commonly used segments for cell separation include:
- Centrifugation: This technique separates cells based on their density and size. Centrifugation can be done by differential centrifugation or density gradient centrifugation.
- Filtration: This technique separates cells based on their size using porous filters with different pore sizes.
- Sedimentation: This technique separates cells based on their sedimentation rates in a medium, such as a sucrose gradient.
- Immunomagnetic cell separation: This technique uses magnetic beads coated with specific antibodies to selectively bind and isolate cells.
- Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS): This technique uses fluorescent markers to label specific cells and a machine to sort them based on their fluorescence signal.
- Microfluidics: This technique uses microchannels to separate cells based on their size, deformability, or other properties.
- Microscopy-based techniques: These techniques use imaging and microscopy to identify and separate cells based on their morphology or other properties.
Overall, the choice of technique depends on the properties of the cells to be separated, the desired purity of the cell population, and the downstream applications of the separated cells.
𝐋𝐞𝐚𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐏𝐥𝐚𝐲𝐞𝐫𝐬:-
Becton Dickinson and Company, GE Healthcare, Merck KgaA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc, Terumo BCT, PluriSelect Life Science UG & Co. KG, MiltenyiBiotec, Beckman Coulter, Inc., STEMCELL Technologies Inc.
Request Customization: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-for-customization/14228
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬:
Allied Market Research (AMR) is a full-service market research and business-consulting wing of Allied Analytics LLP based in Portland, Oregon. Allied Market Research provides global enterprises as well as medium and small businesses with unmatched quality of “Market Research Reports” and “Business Intelligence Solutions.” AMR has a targeted view to provide business insights and consulting to assist its clients to make strategic business decisions and achieve sustainable growth in their respective market domain.